Introduction
Blockchain networks and smart contracts are tamper-proof, transparent, and secure by nature, but they have one major flaw: they are unable to access real-world data on their own.what is an Oracle This is where oracles come in.
An oracle is a system that pulls external data and brings it onto the blockchain, allowing smart contracts to draw connections to real-world events.
1. What is an Oracle?
An oracle is a gateway between the blockchain and the outside world. Because blockchains are closed systems, they cannot directly use external data, including:
Market prices (e.g., cryptocurrency or stock prices)
Weather conditions (for insurance smart contracts)
Sports results (for blockchain-based betting platforms)
IoT (Internet of Things) data (for supply chain tracking)
2. Why Are Oracles Important?
Without oracles, smart contracts would only be able to use on-chain data. Oracles allow:
✔ Automation – Smart contracts can operate based on real-world data.
✔ Real-World Integration – Allows blockchains to interact with external systems.
✔ Decentralized Finance (DeFi) – Provides real-time price feeds for lending, borrowing, and trading.
✔ Smart Insurance – Weather oracles can trigger payments when storm reports happen.
https://affilipro.online/2321-2/
3. Types of Oracles
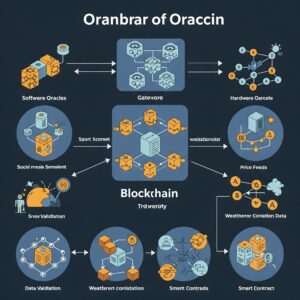
1. Blockchain Oracles
Blockchain oracles give real-world information to smart contracts. They can be:
Software Oracles – Extract data from APIs, websites, or databases (e.g., weather, stocks).
Hardware Oracles – Extract data from hardware devices like IoT sensors or RFID scanners.
Inbound Oracles – Extract external data into the blockchain (e.g., election results, sports scores).
Outbound Oracles – Push data from the blockchain to outside systems (e.g., initiating a bank transaction).
Consensus-based Oracles – Gather information from various sources in order to make it correct.
2. Mythological Oracles
Mythological oracles are a person or a place that gives godly or supernatural answers. Some examples include:
Pythia (Oracle of Delphi) – Ancient Greek priestess who provided prophecies by Apollo.
Sibyls – Greco-Roman women prophets.
Chinese Oracles (I Ching) – Practiced divinatory techniques like casting yarrow sticks.
3. Computing and Database Oracles
Oracle Database – A database management system by Oracle Corporation.
Test Oracles – Operations that determine software tests pass or fail on the basis of predicted and actual outputs.
4. How Oracles Work
1. Data Request – A smart contract asks for external data.
2. Oracle Retrieves Data – The oracle retrieves data from an external data source (e.g., an API).
3. Verification – The oracle checks the integrity of the data (especially in decentralized oracles).
4. Transmission of Data – The oracle sends the verified data back to the blockchain.
5. Execution by Smart Contract – The smart contract performs an action depending on the processed data.
5. Applications of Oracles
A. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
✔ Price feeds for lending/borrowing (Aave, Compound).
✔ Market data automated trading strategies.
B. Supply Chain & Logistics
✔ Tracking products using IoT sensors.
✔ Verifying the origin of products.
C. Insurance & Weather Data
✔ Insurance claims issued by smart contracts based on weather data.
D. Gaming & Sports Betting
✔ Blockchain-based betting platforms that verify game results.Reddit ·
http://Reddit · r/gaming45.7M+ followersr/gaming
6. Risks and Challenges
❌ Data Manipulation (Oracle Problem) – Oracles must be trusted in order to provide correct data.
❌ Centralization Risks – A centralized oracle represents a sole point of failure.
❌ Smart Contract Dependencies – In the event of the oracle’s failure, the smart contract cannot be executed.
7. Conclusion
Oracles play a significant role in blockchain technology, and that is providing the ability to interact with the outside world through smart contracts. However, oracles pose risks to security, thus decentralized oracles like Chainlink and API3 are on the forefront to make oracles more trustworthy.